|
Lambda
Lambda (; uppercase , lowercase ; , ''lám(b)da'') is the eleventh letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed. Lambda gave rise to the Latin L and the Cyrillic El (Л). The ancient grammarians and dramatists give evidence to the pronunciation as () in Classical Greek times. In Modern Greek, the name of the letter, Λάμδα, is pronounced . In early Greek alphabets, the shape and orientation of lambda varied. Most variants consisted of two straight strokes, one longer than the other, connected at their ends. The angle might be in the upper-left, lower-left ("Western" alphabets) or top ("Eastern" alphabets). Other variants had a vertical line with a horizontal or sloped stroke running to the right. With the general adoption of the Ionic alphabet, Greek settled on an angle at the top; the Romans put the angle at the lower-left. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda Particle
The lambda baryons (Λ) are a family of subatomic hadron particles containing one up quark, one down quark, and a third quark from a higher flavour generation, in a combination where the quantum wave function changes sign upon the flavour of any two quarks being swapped (thus slightly different from a neutral sigma baryon, ). They are thus baryons, with total isospin of 0, and have either neutral electric charge or the elementary charge +1. Overview The lambda baryon was first discovered in October 1950, by V. D. Hopper and S. Biswas of the University of Melbourne, as a neutral V particle with a proton as a decay product, thus correctly distinguishing it as a baryon, rather than a meson, i.e. different in kind from the K meson discovered in 1947 by Rochester and Butler; they were produced by cosmic rays and detected in photographic emulsions flown in a balloon at . Though the particle was expected to live for , it actually survived for . The property that caused it to liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Von Mangoldt Function
In mathematics, the von Mangoldt function is an arithmetic function named after German mathematician Hans von Mangoldt. It is an example of an important arithmetic function that is neither multiplicative nor additive. Definition The von Mangoldt function, denoted by , is defined as :\Lambda(n) = \begin \log p & \textn=p^k \text p \text k \ge 1, \\ 0 & \text \end The values of for the first nine positive integers (i.e. natural numbers) are :0 , \log 2 , \log 3 , \log 2 , \log 5 , 0 , \log 7 , \log 2 , \log 3, which is related to . Properties The von Mangoldt function satisfies the identityApostol (1976) p.32Tenenbaum (1995) p.30 :\log(n) = \sum_ \Lambda(d). The sum is taken over all integers that divide . This is proved by the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, since the terms that are not powers of primes are equal to . For example, consider the case . Then :\begin \sum_ \Lambda(d) &= \Lambda(1) + \Lambda(2) + \Lambda(3) + \Lambda(4) + \Lambda(6) + \Lambda(12) \\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epichoric Alphabets
Many local variants of the Greek alphabet were employed in ancient Greece during the Archaic Greece, archaic and Classical Greece, early classical periods, until around 400 BC, when they were replaced by the classical 24-letter alphabet that is the standard today. All forms of the Greek alphabet were originally based on the shared inventory of the 22 symbols of the Phoenician alphabet, with the exception of the letter Samekh, whose Greek counterpart Xi (letter), Xi () was used only in a subgroup of Greek alphabets, and with the common addition of Upsilon () for the vowel . The local, so-called ''epichoric'', alphabets differed in many ways: in the use of the consonant symbols , and ; in the use of the innovative long vowel letters ( and ), in the absence or presence of Η in its original consonant function (); in the use or non-use of certain archaic letters ( = , = , = ); and in many details of the individual shapes of each letter. The system now familiar as the standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigendecomposition Of A Matrix
In linear algebra, eigendecomposition is the factorization of a matrix into a canonical form, whereby the matrix is represented in terms of its eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Only diagonalizable matrices can be factorized in this way. When the matrix being factorized is a normal or real symmetric matrix, the decomposition is called "spectral decomposition", derived from the spectral theorem. Fundamental theory of matrix eigenvectors and eigenvalues A (nonzero) vector of dimension is an eigenvector of a square matrix if it satisfies a linear equation of the form \mathbf \mathbf = \lambda \mathbf for some scalar . Then is called the eigenvalue corresponding to . Geometrically speaking, the eigenvectors of are the vectors that merely elongates or shrinks, and the amount that they elongate/shrink by is the eigenvalue. The above equation is called the eigenvalue equation or the eigenvalue problem. This yields an equation for the eigenvalues p\left(\lambda\right) = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Bruijn–Newman Constant
The de Bruijn–Newman constant, denoted by \Lambda and named after Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn and Charles Michael Newman, is a mathematical constant defined via the zeros of a certain function H(\lambda,z), where \lambda is a real parameter and z is a complex variable. More precisely, :H(\lambda, z):=\int_^ e^ \Phi(u) \cos (z u) \, du, where \Phi is the super-exponentially decaying function :\Phi(u) = \sum_^ (2\pi^2n^4e^-3\pi n^2 e^ ) e^ and \Lambda is the unique real number with the property that H has only real zeros if and only if \lambda\geq \Lambda. The constant is closely connected with Riemann hypothesis. Indeed, the Riemann hypothesis is equivalent to the conjecture that \Lambda\leq 0. (announcement post) Brad Rodgers and Terence Tao proved that \Lambda\geq 0, so the Riemann hypothesis is equivalent to \Lambda=0. A simplified proof of the Rodgers–Tao result was later given by Alexander Dobner. History De Bruijn showed in 1950 that H has only real zeros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as well as consonants. In Archaic Greece, Archaic and early Classical Greece, Classical times, the Greek alphabet existed in Archaic Greek alphabets, many local variants, but, by the end of the 4th century BC, the Ionia, Ionic-based Euclidean alphabet, with 24 letters, ordered from alpha to omega, had become standard throughout the Greek-speaking world and is the version that is still used for Greek writing today. The letter case, uppercase and lowercase forms of the 24 letters are: : , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , The Greek alphabet is the ancestor of several scripts, such as the Latin script, Latin, Gothic alphabet, Gothic, Coptic script, Coptic, and Cyrillic scripts. Throughout antiquity, Greek had only a single uppercas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El (Cyrillic)
El (Л л or Ʌ ʌ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. El commonly represents the alveolar lateral approximant . In Slavic languages it may be either palatalized or slightly velarized; see below. History The Cyrillic letter El was derived from the Greek letter lambda (Λ λ). In the Early Cyrillic alphabet its name was (''ljudije''), meaning "people". In the Cyrillic numeral system, Л had a value of 30. Forms El has two forms: one form resembles Greek capital Lambda (Ʌ ʌ), and the other form resembles the Hebrew letter ת (Л л). In some typeface A typeface (or font family) is a design of Letter (alphabet), letters, Numerical digit, numbers and other symbols, to be used in printing or for electronic display. Most typefaces include variations in size (e.g., 24 point), weight (e.g., light, ...s the Cyrillic letter El has a grapheme which may be confused with the Cyrillic letter Pe (П п). Note that Pe has a straight left leg, without the hoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Likelihood Function
A likelihood function (often simply called the likelihood) measures how well a statistical model explains observed data by calculating the probability of seeing that data under different parameter values of the model. It is constructed from the joint probability distribution of the random variable that (presumably) generated the observations. When evaluated on the actual data points, it becomes a function solely of the model parameters. In maximum likelihood estimation, the argument that maximizes the likelihood function serves as a point estimate for the unknown parameter, while the Fisher information (often approximated by the likelihood's Hessian matrix at the maximum) gives an indication of the estimate's precision. In contrast, in Bayesian statistics, the estimate of interest is the ''converse'' of the likelihood, the so-called posterior probability of the parameter given the observed data, which is calculated via Bayes' rule. Definition The likelihood function, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
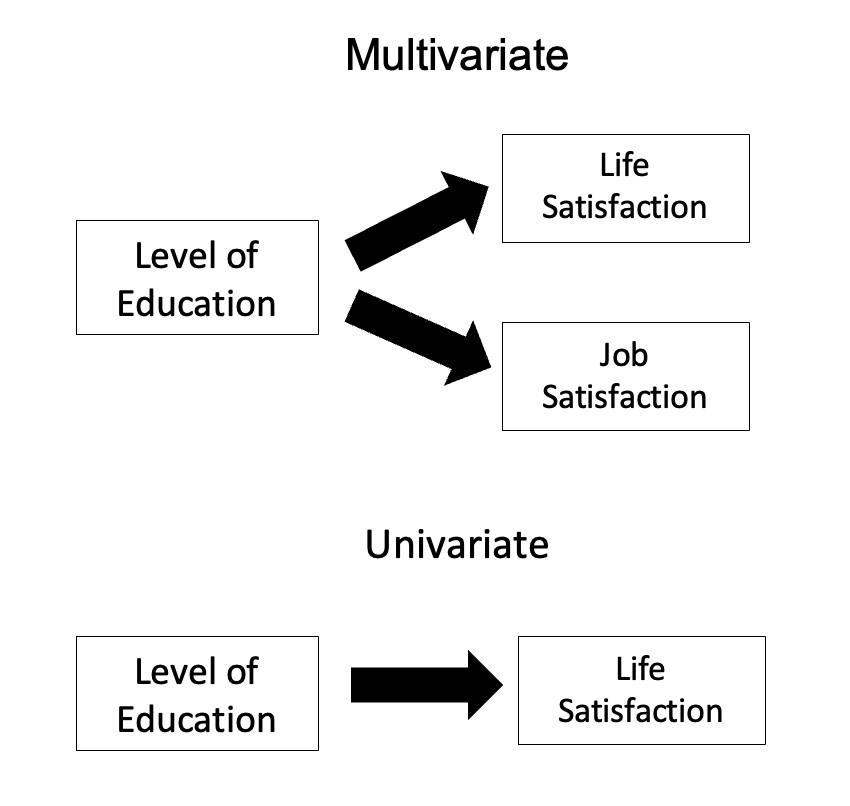
MANOVA
In statistics, multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) is a procedure for comparing multivariate sample means. As a multivariate procedure, it is used when there are two or more dependent variables, and is often followed by significance tests involving individual dependent variables separately. Without relation to the image, the dependent variables may be k life satisfactions scores measured at sequential time points and p job satisfaction scores measured at sequential time points. In this case there are k+p dependent variables whose linear combination follows a multivariate normal distribution, multivariate variance-covariance matrix homogeneity, and linear relationship, no multicollinearity, and each without outliers. Model Assume n q-dimensional observations, where the i’th observation y_i is assigned to the group g(i)\in \ and is distributed around the group center \mu^\in \mathbb R^q with multivariate Gaussian noise: y_i = \mu^ + \varepsilon_i\quad \varepsilon_i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenvalues
In linear algebra, an eigenvector ( ) or characteristic vector is a vector that has its direction unchanged (or reversed) by a given linear transformation. More precisely, an eigenvector \mathbf v of a linear transformation T is scaled by a constant factor \lambda when the linear transformation is applied to it: T\mathbf v=\lambda \mathbf v. The corresponding eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root is the multiplying factor \lambda (possibly a negative or complex number). Geometrically, vectors are multi-dimensional quantities with magnitude and direction, often pictured as arrows. A linear transformation rotates, stretches, or shears the vectors upon which it acts. A linear transformation's eigenvectors are those vectors that are only stretched or shrunk, with neither rotation nor shear. The corresponding eigenvalue is the factor by which an eigenvector is stretched or shrunk. If the eigenvalue is negative, the eigenvector's direction is reversed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Numerals
Greek numerals, also known as Ionic, Ionian, Milesian, or Alexandrian numerals, is a numeral system, system of writing numbers using the letters of the Greek alphabet. In modern Greece, they are still used for ordinal number (linguistics), ordinal numbers and in contexts similar to those in which Roman numerals are still used in the Western world. For ordinary cardinal number (linguistics), cardinal numbers, however, modern Greece uses Arabic numerals. History The Minoans, Minoan and Mycenaean civilizations' Linear A and Linear B alphabets used a different system, called Aegean numerals, which included number-only symbols for powers of ten: = 1, = 10, = 100, = 1000, and = 10000. Attic numerals composed another system that came into use perhaps in the 7th century BC. They were acrophonic, derived (after the initial one) from the first letters of the names of the numbers represented. They ran = 1, = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subatomic Particle
In physics, a subatomic particle is a particle smaller than an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a baryon, like a proton or a neutron, composed of three quarks; or a meson, composed of two quarks), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, quarks; or electrons, muons, and tau particles, which are called leptons). Particle physics and nuclear physics study these particles and how they interact. Most force-carrying particles like photons or gluons are called bosons and, although they have quanta of energy, do not have rest mass or discrete diameters (other than pure energy wavelength) and are unlike the former particles that have rest mass and cannot overlap or combine which are called fermions. The W and Z bosons, however, are an exception to this rule and have relatively large rest masses at approxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |